A man’s penis is an important part of his identity as a man. It serves a critical role in urinary function. Its function as a sexual organ is also important; sexuality is a source of physical pleasure, emotional bonding, and procreation.
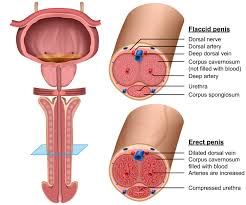
The penis is a cylindrical organ consisting of three separate chambers. On the upper (dorsal) portion of the penis there are two corpora cavernosa that are surrounded by a tough but elastic layer of connective tissue called the tunica albuginea. The third chamber is called the corpus spongiosum; it is located below the corpora cavernosa and is surrounded by a thin connective tissue sheath. It contains the urethra, the narrow tube that carries urine and semen out of the body.
These three chambers are made up of highly specialized, sponge-like erectile tissue filled with thousands of venous cavities, spaces that contain very little blood when the penis is soft. During erection, blood fills these cavities, causing the corpora cavernosa to balloon and push against the tunica albuginea. While the penis hardens and stretches, the skin and connective tissue of the penis remain loose and elastic to accommodate the changes.
5 most common diagnosis of the Penis:
- Peyronies Disease (PD)
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- STD or STI checks/screenings
- Adult Circumcision
- Premature Ejaculation or Retrograde Ejaculation
For an alphabetical listing of all the urological conditions we treat click here.

